| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
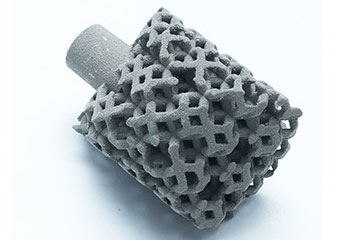
| Technology Name | 바인더 분사 (BJ) |
| Basic Principle | A liquid binding agent is selectively deposited by an industrial printhead onto thin layers of powdered material (e.g., metals, ceramics, sand), bonding particles layer by layer to form a 3D object. |
| Materials Used |
Metals: Stainless steel, Inconel, copper, titanium, bronze-based alloys. Ceramics: Silica, alumina, zirconia, calcium phosphate. Polymers: 나일론, PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate). Sand: Foundry sand for casting molds. Composites: Metal-ceramic or polymer-ceramic hybrids. |
| Process Workflow | 1. Spread a powder layer → 2. Printhead jets binder to bond particles → 3. Lower build platform → 4. Repeat until object is complete → 5. Post-processing (curing, sintering, or infiltration) may be required. |
| Key Advantages |
– High speed and scalability for mass production. – Low cost compared to other 3D printing methods. – No support structures needed. – Capable of full-color printing using colored binders. – Wide material compatibility (metals, ceramics, polymers, sand). |
| Common Applications |
– Metal parts for aerospace and automotive industries. – Ceramic components (e.g., tooling, medical devices). – Sand molds for casting. – Full-color prototypes and architectural models. |
| 제한사항 |
– Parts may require post-processing (e.g., sintering) for full density and strength. – Surface finish may be rougher than laser-based methods. – Minimal feature resolution limited by powder particle size. |
| Historical Context | Invented at MIT in the early 1990s and later commercialized by companies like Z Corporation (acquired by 3D Systems) and ExOne. |